We’re thrilled to announce that The OX Active ASPM platform is now fully integrated with GitLab. With this integration, users no longer have to choose between rapid deployment or security in their software development. GitLab’s comprehensive web-based platform, known for its source control, issue tracking, and CI/CD capabilities, now enhances its offering with OX’s automated security scans. This means developers can embed security directly into their DevOps workflow, streamlining processes while maintaining high-security standards.
This blog post will explain how the OX and GitLab integration revolutionizes DevSecOps by embedding Application Security Testing (AST) seamlessly into the CI/CD process, enabling developers to conduct comprehensive security assessments effortlessly within their development environment.
Understanding GitLab’s Role in DevOps
GitLab stands out as a versatile DevOps lifecycle tool. It provides a Git repository manager that supports wiki, issue-tracking, and, importantly, CI/CD pipeline features. These capabilities make it an invaluable asset for teams to streamline their development processes while ensuring high-quality outputs.
The Power of Connecting OX with GitLab
Integrating OX with GitLab enhances security by automating application vulnerability scans. OX directly maps out applications from GitLab, conducting thorough security scans to identify and address potential issues early in development. Additionally, OX consolidates and prioritizes issues to minimize noise and enhance accuracy, enabling developers to concentrate on their deliverables.
How to Connect Your GitLab with OX
For Public SaaS GitLab Server Users:
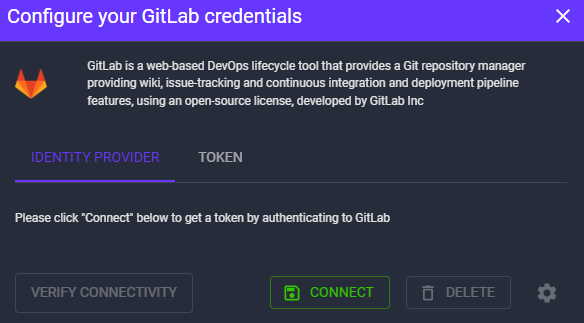
If you’re utilizing the public SaaS version of GitLab (gitlab.com), you have two options for connecting with OX: using an “Identity Provider” or a “Token.”
- Identity Provider: This method is straightforward—simply click “Connect” under the “Identity Provider” tab and follow the on-screen instructions.
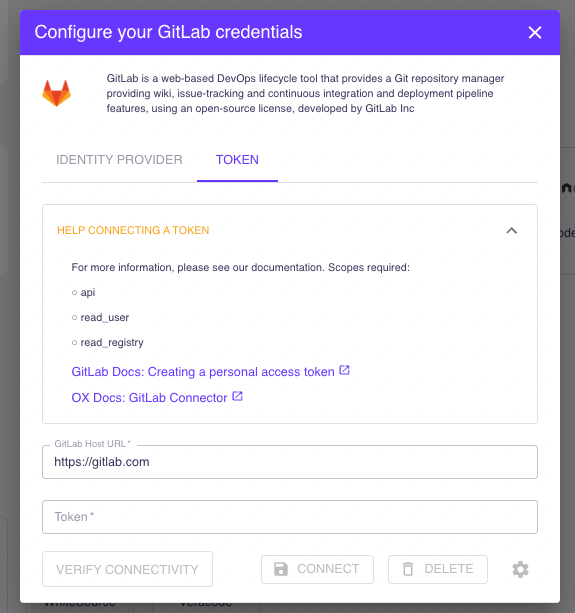
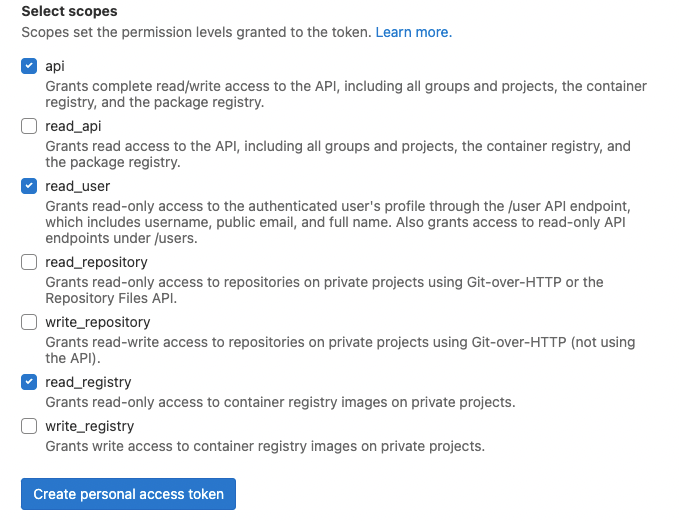
- Token: For this option, you must create a token within GitLab endowed with specific permissions (or scopes), namely api, read_user, and read_registry. Once created, copy this token into the designated field on the “Token” login tab, which is set to the address of the SaaS server by default, and click “Connect.”
For GitLab Enterprise Users:
Those with a private GitLab installation will use the “Token” login method. On the ” Token ” login tab, you must provide your GitLab server URL and the token with the required scopes.
Setting Up Repositories for Scanning
After establishing connectivity between GitLab and OX, you’ll have the ability to view all your repositories. You can select which ones you want OX to scan for security issues here.
- Configuring Repositories’ Scope: Utilize the “Gear” icon to specify which repositories OX should scan. This setting ensures that only selected repositories are included in the security scan.
- Managing New Repositories: You also have the option to set default actions for any newly discovered repositories, deciding whether they should be automatically included in future scans.
You can view a step-by-step guide here.
The Outcome
By integrating OX with GitLab, developers can significantly enhance the security of their applications without disrupting the flow of their DevOps processes. This powerful combination not only automates security checks but also ensures that potential vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated early, paving the way for more secure software deployment.
This integration exemplifies how security can be seamlessly woven into the fabric of software development, offering peace of mind to developers and stakeholders alike. With the continuous evolution of cyber threats, the importance of such integrations cannot be overstated, making the GitLab and OX partnership a crucial step forward in pursuing secure software development in the era of rapid deployments.






)


